Access resistances in vertical devices
There is an “access” resistance connected in series with an “ideal” diode “D” (the diode can be of any type, i.e. rectifier, LED, Varicap, Tunnel diode etc.).
Total access (series) resistance for the diode on the left:
Note the difference between lateral and vertical contacts. For lateral contacts, a unit-width contact resistance (Ω×mm or Ω×cm) is typically used. For vertical contacts, a unit-area specific resistance (Ω×mm2 or ×cm2) is typically used.
Access resistances in vertical devices (cont.)
The series resistance associated with the diode base regions: Rsp and Rsn
Access resistances in vertical devices (cont.)
Diode low-frequency equivalent circuit
Access resistances in vertical devices (cont.)
Diode low-frequency equivalent circuit
Access resistances in lateral devices
Example: planar GaAs Schottky diode
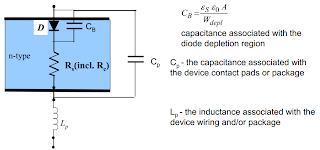
High-frequency equivalent circuits
Example: vertical Schottky diode
At high frequencies, capacitances and inductances associated with the diode itself and the package have significant impact on the device performance













0 comments