Specially designed to provide a
reliable end to end byte stream over a unreliable network The inter network
differs from a single network in terms of topology and bandwidth delay packet
size. TCP adapts to properties of such network. Each machine supporting TCP has
TCP entity. IP layer provide no guarantee that the datagrams will be delivered so
the TCP has to provide the reliability
TCP
• point-to-point:
– one sender, one receiver
• reliable, in-order byte
steam:
– no “message boundaries”
• pipelined:
– TCP congestion and flow control
set window size at the time of
connection setup
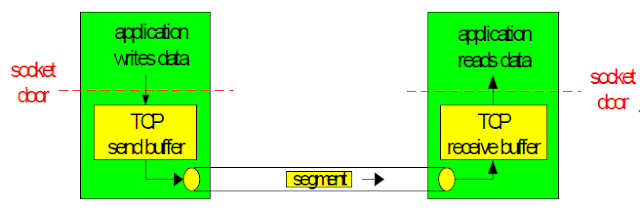
• send & receive buffers the
buffer size negotiated
• full duplex data:
– bi-directional data flow in
same connection
– MSS: maximum segment size
• connection-oriented:
– handshaking (exchange of
control msgs) init’s sender, receiver state before
data exchange
• flow controlled:
– sender will not overwhelm receiver





0 comments