§ The hierarchical approach reduces the size of the
routing tables at the routers in assigning the addresses.
§ Hosts that are near each other (i.e. a group)
should have addresses that have common prefixes. The routers examine only part
of the address (i.e.. the prefix) to decide how a packet should be routed.
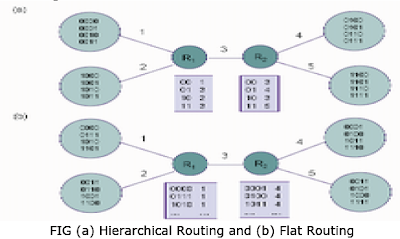
§ Figure below gives an example of hierarchical
address assignment and a flat address assignment.
§ In figure (a) the hosts at each of the four sites
have the same prefix. Thus the two routers need only maintain tables with four
entries as shown.
§ On the other hand, if the addresses are not
hierarchical (Figure), then the routers need to maintain 16 entries in their routing
tables.





0 comments