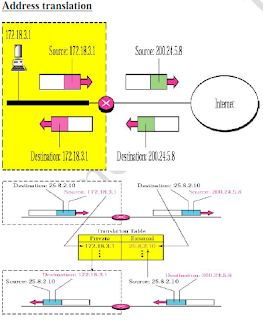
v NAT is the
translation of an Internet Protocol address (IP address) used within one network
to a different IP address known within another network.
v One network is
designated the inside network and the other is the outside.
v Typically, a
company maps its local inside network addresses to one or more global outside
IP addresses and unmaps the global IP addresses on incoming packets back into local
IP addresses.
v This helps
ensure security since each outgoing or incoming request must go through a translation
process that also offers the opportunity to qualify or authenticate the request
or match it to a previous request.
v NAT also
conserves on the number of global IP addresses that a company needs and it lets
the company use a single IP address in its communication with the world.
v NAT is included
as part of a router and is often part of a corporate firewall.
v Network
administrators create a NAT table that does the global-to-local and
local-toglobal IP address mapping.
v NAT can be
statically defined or it can be set up to dynamically translate from and to a pool
of IP addresses.
NAT lets an administrator to
create tables that map:
v A local IP
address to one global IP address statically
v A local IP
address to any of a rotating pool of global IP addresses that a company may have
a local IP address plus a particular TCP port to a global IP address or one in
a pool of them
v A global IP address to
any of a pool of local IP addresses on a round-robin basis






0 comments