• Performance Problems in
Computer Networks
• Network Performance Measurement
• System Design for Better
Performance
• Fast TPDU Processing
• Protocols for Gigabit Networks
Performance
problems in computer networks
• Overloads Example 1: TPDU
containing the bad parameter when broadcast may
clog the n/w results in broadcast
storm due to error message
• synchronous overload due to
power failure-DHCP contacted for booting
• Apart from this problems due to
insufficient memory TPDUs lost
• Not setting the timeout
correctly the TPDUs lost
• Gigabit n/w pose new problems
• The next figure explains this
here the transmission line used only for .5msec
greatly reducing the efficiency
• The useful quantity is the
Bandwidth-Delay product
• The product is the capacity of
the pipe from sender to receiver and back to sender
in bits
• In the above example it is 40
million bits but the actual utilisation is only 1.25
percent of the pipe capacity
• therefore for good performance
the receiver window must be at least as large as
the Bandwidth-Delay product
• Another performance problem
could be jitter to avoid a small standard deviation
is used
The basic loop
for improving network performance.
• Measure relevant network
parameters, performance.
• Try to understand what is going
on.
• Change one parameter
Precautions taken while measuring
• Sample size should be large
enough
• Samples should be
representative
• To be careful while using
coarse grained clock
• Nothing unexpected going on
while tests are conducted
• Caching problem
• Understanding the measurements
• Extrapolation of the result
System Design
for Better Performance
Rules:
• CPU speed is more important
than network speed.
• Reduce packet count to reduce
software overhead.
• Minimize context switches.
• Minimize copying.
• You can buy more bandwidth but
not lower delay.
• Avoiding congestion is better
than recovering from it.
• Avoid timeouts.
Fast TPDU
Processing
• TPDU processing overhead has
two components
• one –overhead per TPDU
• other – overhead per byte
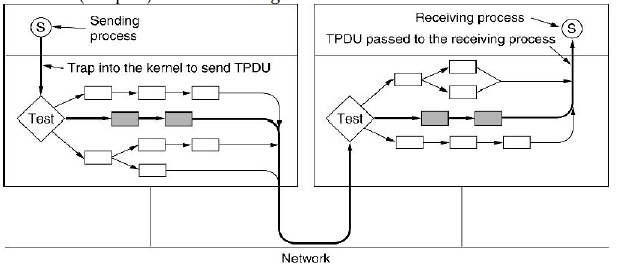
• Example take the sending side
• first the sending side traps to kernel to
SEND
• if it is a normal case then the
state is ESTABLISHED and typically this path is
taken (fast path) shown in the figure below
The fast path from sender to
receiver is shown with a heavy line.
The processing steps on this path
are shaded.
Another example
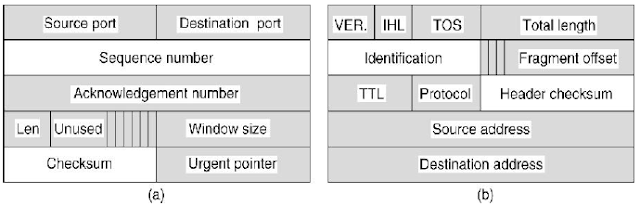
• In the TCP header the fields
that are same between consecutive TPDUs on a one
way flow are shaded
• All sending TCP entity has to
copy from the prototype header into the output
buffer
• It handovers the header and
data to the special IP procedure for sending a regular
max TPDU
• IP then copies its prototype header and makes the
packet ready
the above figure
(a) TCP header. (b) IP header. In
both cases, the shaded fields are taken from the
prototype without change.
Fast path
processing at receiver side
• step 1: locating the connection
record for the incoming TPDU
• The TPDU checked to see if it
is normal case
• If all checks are met then a
fast procedure is called
• Many TCP implementations use
Header Prediction
• The other two areas where major
performance gain are possible are
Buffer management
Timer Management
• The timer management done by
the timing wheel
• There are some problems and the
possible solution posed by the Gigabit protocols
• Problems
Sequence Numbers
Communication Speeds
Go back n protocol and its poor
performance
gigabit lines are bandwidth
limited
Results of new application






0 comments