• How TCP prevents congestion
• when connection established,
window size chosen
• Receiver specifies seeing its
buffer size
• Still congestion occurs
• The two problems are Network
Capacity and Receiver Capacity
• Solution?
• Solution
• Sender maintains two windows:
one the receiver granted
• the other Congestion Window
• at the connection
establishment- the congestion window is set to the size of the
maximum segment in use on the
connection
• Each burst acknowledged doubles
the congestion window
• Congestion window grow
exponentially
• This is called the Slow Start
algorithm
• Another Solution?
• Solution
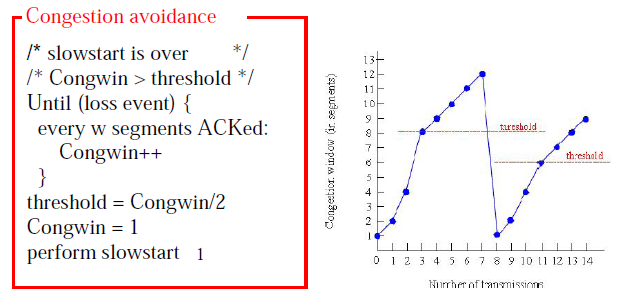
• Uses threshold
• initially some value in
addition to the receiver and congestion window
• When timeout threshold is set
to half of the current congestion window
• Congestion window is set to one
max segment
• Slow start is used to find what
the network can handle
• Exponential growth stops when
threshold hit
• From that point congestion window grow linearly
• Example
• Segment size=1K
• Congwin=64KB
• when timeout threshold=34KB
• Congwin=1KB
• the congstion window grows
exponentially until it hits threshold and then linearly






0 comments