TCP sender, receiver establish “connection”
before exchanging data segments
• initialize TCP variables:
– seq. nubers
– buffers, flow control info
(e.g. RcvWindow)
• client: connection
initiator
Socket clientSocket = new Socket("hostname","port
number");
• server: contacted by
client
Socket connectionSocket =
welcomeSocket.accept();
Three way
handshake
Step 1: client end system sends
TCP SYN control segment to server
– specifies initial seq number
Step 2: server end system receives
SYN, replies with SYNACK control segment
– ACKs received SYN
– allocates buffers
– specifies server-> receiver
initial seq. number
Step 3: client sends the request
and the ack for the server seq number
The three way handshake is over
Connection Release
client closes socket:
clientSocket.close();
Step 1: client end system sends
TCP FIN control segment to server
Step 2: server receives FIN,
replies with ACK. Closes connection, sends FIN
Step 3: client receives FIN,
replies with ACK.
– Enters “timed wait” - will
respond with ACK to received FINs
Step 4: server, receives ACK.
Connection closed.
Note: with small modification,
can handle simultaneous FINs.
The connection management client side
can be shown in a flow diagram
The connection management server side
can be shown in a flow diagram
Connection
management
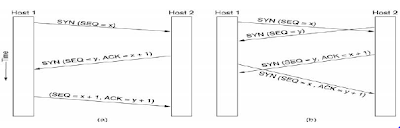
The two figures
(a) TCP connection establishment
in the normal case.
(b) Call collision.
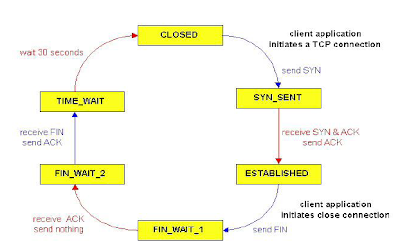
• TCP connection management
finite state machine.
• The heavy solid line is the
normal path for a client.
• The heavy dashed line is the
normal path for a server.
• The light lines are unusual
events.
• Each transition is labeled by
the event causing it and the action resulting from it, separated by a slash.








0 comments